The MigratoryData JWT Authorization add-on allows you to authorize users to subscribe to and/or publish real-time messages on specific subjects using the JSON Web Tokens (JWT) standard. The add-on is preinstalled in the MigratoryData server starting with version 6.0.9 and its source code is freely available on GitHub. It is built using the Server Extensions API for Authorization.
Overview
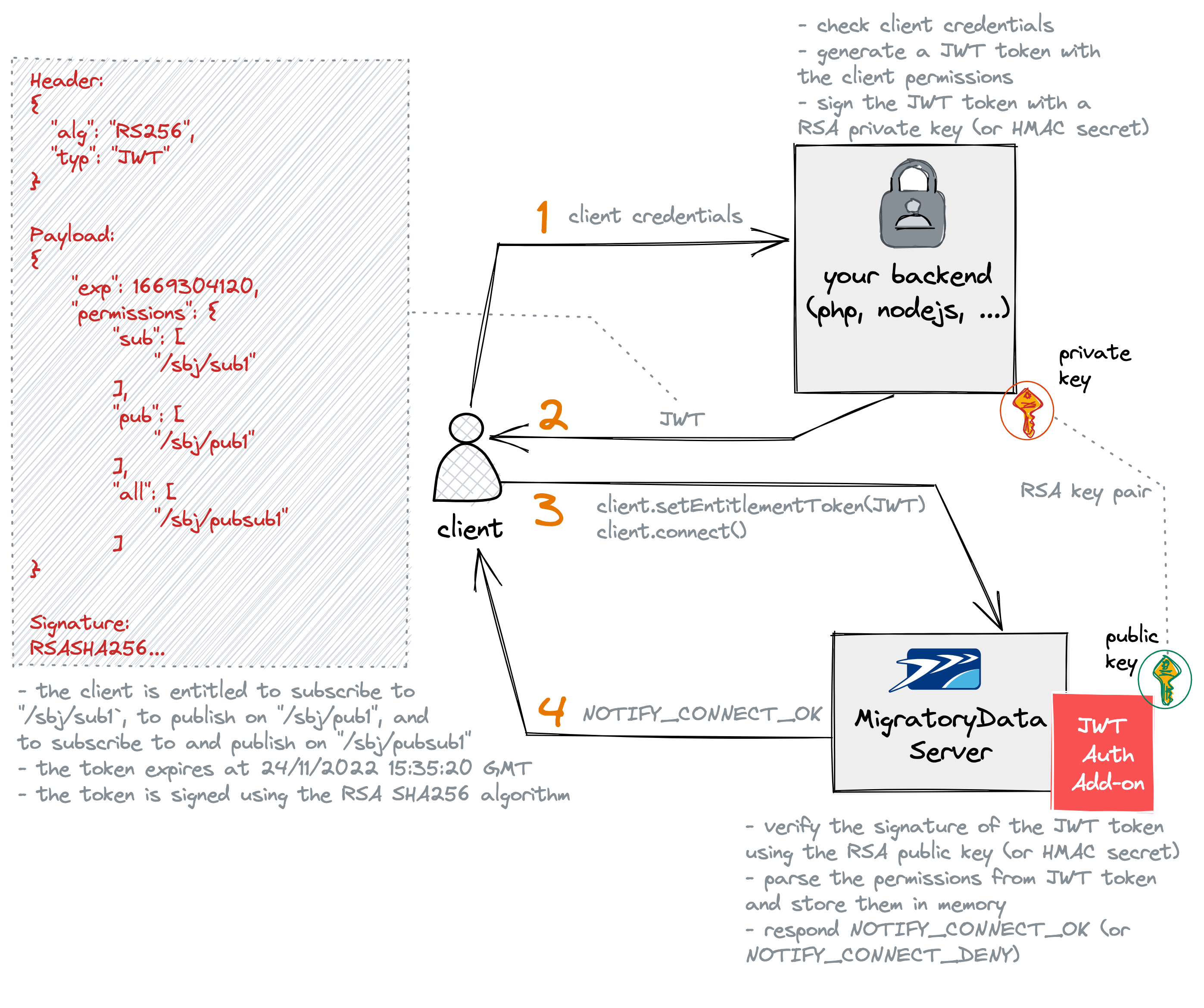
The following diagram highlights the JWT authorization workflow with MigratoryData.
-
Your client application connects to your backend services to request a JWT token. The client application typically provides the login credentials, such as the username and password of the user who opened the client application.
-
Your backend checks the login credentials of the user and retrieves the client’s permissions, typically from a database.
Then, it should generate a JWT token with the payload containing several standard and custom fields, also referred to as claims. The JWT token must include at least the standard claimexpcontaining the expiration time of the token, expressed in seconds as epoch time. It must also include the custom claimpermissionscontaining the permissions of the client using the following JSON format:
"permissions": {
"sub": [
"/subject/sub1",
"/subject/sub2"
],
"pub": [
"/subject/pub1",
"/subject/pub2",
"/subject/pub3"
],
"all": [
"/subject/pubsub1",
"/subject/pubsub2"
]
}
where the subfield sub defines the subjects to which the client is authorized to subscribe, the subfield pub defines
the subjects on which the client is authorized to publish, and the subfield all defines the subjects on which the
client is authorized to both publish and subscribe.
Finally, before sending the JWT token to the client application, the JWT token needs to be signed either with an
HMAC secret or an RSA private key. Both the symmetric signature using HMAC algorithms and the asymmetric signature using
RSA algorithms are supported as further detailed in the documentation of the parameter signature.type.
-
Once the client gets the JWT token from your backend services, it attempts to connect to the MigratoryData server by providing the JWT token with the MigratoryData client API method
setEntitlementToken(). -
The JWT Authorization add-on of the MigratoryData server verifies the signature of the JWT token either with an HMAC secret if the JWT token was signed using an HMAC algorithm, or with an RSA public key if the JWT token was signed using an RSA algorithm. If correct, it parses the permissions from the JWT token and store them in memory for subsequent publish and subscribe authorization requests. Finally, if both the signature verification and permission parsing are successful, then the add-on sends a notification
NOTIFY_CONNECT_OKto the client, or otherwise it sends a notificationNOTIFY_CONNECT_DENY.
Enabling the add-on
The JWT Authorization add-on is preinstalled in the MigratoryData server under the following folder, according to the package type used to install the MigratoryData server:
| Location | Package type |
|---|---|
addons/authorization-jwt |
Platform-independent tarball package |
/usr/share/migratorydata/addons/authorization-jwt |
RPM or DEB Linux package |
To enabled it, set the parameter Entitlement of the MigratoryData server on JWT.
Configuring the add-on
The default configuration is available under the following folder:
| Location | Package type |
|---|---|
addons/authorization-jwt |
Platform-independent tarball package |
/etc/migratorydata/addons/authorization-jwt |
RPM or DEB Linux package |
It includes the parameters described below.
renewTokenBeforeSeconds
renewTokenBeforeSeconds |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Specify the number of seconds before a token expiry when to send a token renew notification to the client |
| Default value | 60 |
| Required parameter | Optional |
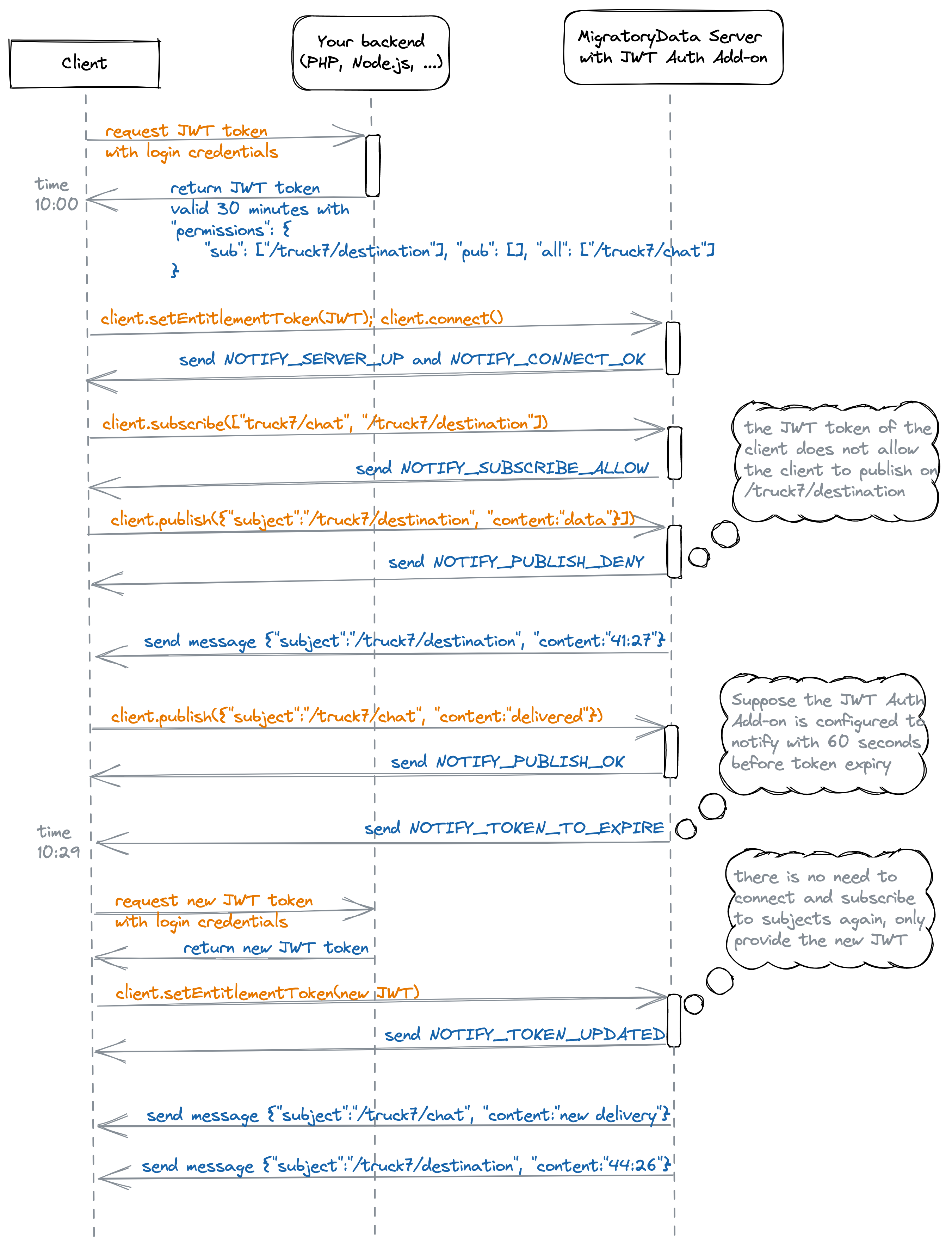
When a JWT token is about to expire, a notification is sent to the client by the JWT Authorization add-on to renew its JWT token. The notification is sent to the client with the number of seconds configured by this parameter before the JWT token expiry.
signature.type
signature.type |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Specify the signing algorithm to be used to verify the JWT tokens, either hmac or rsa |
| Default value | hmac |
| Required parameter | Optional |
Currently, the available signature types are the following ones:
hmac - a symmetric signature method using a single secret key both for signing and verifying JWT tokens. The signature
algorithms supported by this method, automatically selected according to the length of the secret key, are as follows:
- HS256 (HMAC SHA256), requires a 32-byte secret - recommended for most use cases
- HS384 (HMAC SHA384), requires a 48-byte secret
- HS512 (HMAC SHA512), requires a 64-byte secret
rsa - an asymmetric signature method using a pair of public and private keys, where the private key is used for
signing a JWT token, and the public key is used for verifying a JWT token. The signature algorithms supported by
this method, automatically selected according to the length of the private key, are as follows:
- RS256 (RSA SHA256), requires a 2048-bit private key - recommended for most use cases
- RS384 (RSA SHA384), requires a 3072-bit private key
- RS512 (RSA SHA512), requires a 4096-bit private key
signature.hmac.secret
signature.hmac.secret |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Specify the secret key for hmac signature verification |
| Default value | none |
| Required parameter | Mandatory (if the parameter signature.type is set on hmac) |
If your signature type is hmac, configure this parameter with a base64-encoded secret key for verifying the JWT
tokens of your clients. The length of this secret key determines the signature algorithm to be used as explained in the
documentation of the parameter signature.type. For most cases, a 32-byte secret key is recommended.
You can generate a 32-byte secret key encoded as base64 using the command:
openssl rand -base64 32
signature.rsa.publicKeyPath
signature.rsa.publicKeyPath |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Specify the file path of the public key for rsa signature verification |
| Default value | none |
| Required parameter | Mandatory (if the parameter signature.type is set on rsa) |
If your signature type is rsa, configure this parameter with the file path of the public key for verifying the
JWT tokens of your clients. The size in bits of the private key corresponding to the public key determines the signature
algorithm to be used as explained in the documentation of the parameter signature.type. For most cases, a 2048-bit
private key is recommended. You can generate a private key for signing your JTW tokens using this command:
openssl genrsa \
-out rsa-private-key.pem \
2048
Then, extract the public key from the private key — to be configured with this parameter — as follows:
openssl rsa -in rsa-private-key.pem \
-pubout \
-outform PEM \
-out rsa-public-key.pem
Generating JWT tokens on your backend
According to the language you are using for your backend services, please find below examples on how to generate JWT tokens with PHP and Node.js. If your backend services use another language, you should be able to easily adapt those examples to your language or otherwise get in touch with us.
Handling JWT tokens on the client side
The JWT Authorization add-on sends the following notifications to the client application:
| Add-on Notification | Description |
|---|---|
NOTIFY_TOKEN_INVALID |
Notify the client that the JWT token it provided is invalid |
NOTIFY_TOKEN_EXPIRED |
Notify the client that the JWT token it provided is expired |
NOTIFY_TOKEN_TO_EXPIRE |
Notify the client that its JWT token is about to expire and needs to be renewed. This notification is sent with the number of seconds defined by renewTokenBeforeSeconds before the token expiry |
NOTIFY_TOKEN_UPDATED |
Notify the client that the new JWT token it provided has been taken into account by the add-on, i.e. the token renewal was successful |
The client application also receives a number of notifications from the MigratoryData server. Here are several of these notifications related to authentication and authorization:
| Server Notification | Description |
|---|---|
NOTIFY_SERVER_UP |
Notify the client that its WebSocket connection with the MigratoryData server has been established |
NOTIFY_SERVER_DOWN |
Notify the client that its WebSocket connection with the MigratoryData server failed |
NOTIFY_CONNECT_OK |
Notify the client it authenticated successfully with the JWT Authorization add-on or with a custom authorization extension built using the Authorization API v2 |
NOTIFY_CONNECT_DENY |
Notify the client it failed to authenticate with the JWT Authorization add-on or with a custom authorization extension built using the Authorization API v2 for the reason provided in the details of the notification |
NOTIFY_SUBSCRIBE_ALLOW |
Notify the client it successfully subscribed to the subject provided in the details of the notification |
NOTIFY_SUBSCRIBE_DENY |
Notify the client it failed to subscribe to the subject provided in the details of the notification |
NOTIFY_PUBLISH_OK |
Notify the client it successfully published a message with the message ID provided in the details of the notification |
NOTIFY_PUBLISH_DENY |
Notify the client it failed to publish a message with the message ID provided in the details of the notification |
The following sequence diagram details the workflow of these notifications using an example:
We provide the source code of a client application handling JWT tokens on github. This client application is written using MigratoryData Client API for Java. You should be able to easily adapt it to any other language or otherwise please get in touch with us.
