In this article we provide a step-by-step guide to getting started with MigratoryData and its Kafka Native Add-on, an ultra-scalable Websocket publish/subscribe broker which integrates natively with Apache Kafka. Thanks to its huge vertical scalability (1000x more scalable than the C10K problem) and linear horizontal scalability both for publishers and subscribers, MigratoryData can enable bidirectional messaging communication between Apache Kafka and millions of Web and Mobile users or IoT devices - and do so cost-effectively.
Topics and Subjects
We’ve already explained why MigratoryData is a perfect fit for extending Apache Kafka to the Internet, reliably and at scale, as well as the compatibility and complementarity between the two messaging systems.
It is sufficient to say here that both systems MigratoryData and Kafka are publish/subscribe messaging systems, both using a similar notion - named topic in Kafka and subject in MigratoryData - to connect subscribers and publishers. Both Kafka topics and MigratoryData subjects are strings of characters with the following restrictions:
- A Kafka topic can be any string of up to 255 of the following ASCII characters
a-z,A-Z,0-9,.(dot),_(underscore), and-(dash), e.g.vehicles - A MigratoryData subject can be any string starting with
/(slash), and consisting of one or more substrings of any UTF-8 characters excluding/(slash), named segments, separated between them by/(slash), e.g./vehicles/car1/speed
Topics/Subjects Mapping
We use a simple convention to dynamically map between Kafka topics and MigratoryData subjects. The first segment of the
MigratoryData subject corresponds to a Kafka topic, and the remaining segments of the subject correspond to a Kafka key. Therefore, in MigratoryData, the first segment of a subject, corresponding to a Kafka topic, must use at most 255 of the
following ASCII characters permitted by the Kafka topics, i.e. [a-zA-Z0-9_-]. The subsequent segments of the subject,
corresponding to a Kafka key, can use any UTF-8 characters as there are no restrictions for the keys in Kafka.
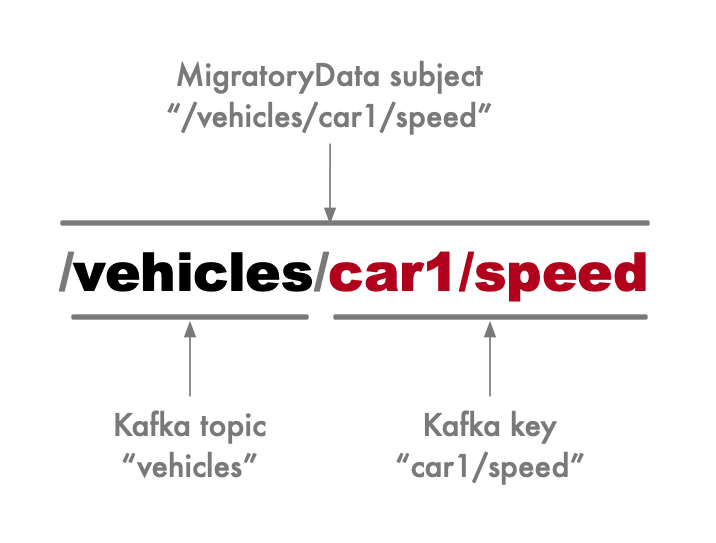
For example, the following MigratoryData subject /vehicles/car1/speed corresponds to the Kafka topic vehicles and the
Kafka key car1/speed as illustrated here:
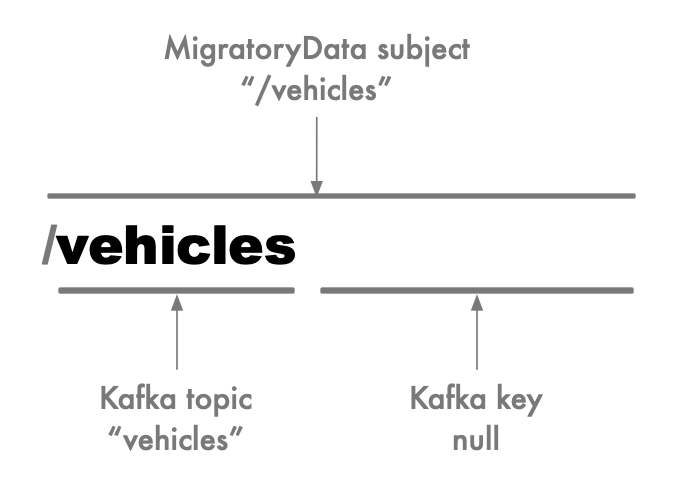
Because in Kafka it is possible to publish a message on a topic, say vehicles, without using a key, i.e. using a null
key, then the Kafka topic vehicles corresponds to the MigratoryData subject /vehicles, consisting only of the
first segment without using any subsequent segments:
Installing Kafka and MigratoryData
MigratoryData comes with installers for Linux and instructions on how to deploy in production MigratoryData clusters either on premises or in the cloud, using Docker and Kubernetes. Also, a platform-independent tarball useful for development and testing on platforms like Linux, Windows, MacOS is available.
Apache Kafka is available from production-ready cloud services like Confluent or Azure Event Hubs. Also, a platform-independent tarball useful for development and testing on platforms like Linux, Windows, MacOS is available.
The only requirement both for MigratoryData and Apache Kafka is to have installed Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 8 or later.
Deploying Kafka
Make sure that you have Java version 8 or later installed. Download the platform-independent tarball
package of Apache Kafka and unzip it to any folder,
change to that folder, and run the following two commands in two different terminals on Linux or MacOS (run the similar
commands with the bat extension instead of the sh extension on Windows):
./bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties
./bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
This will deploy a cluster of one instance of Apache Kafka which will listen for Kafka producers and consumers on
localhost, on the default port 9092.
Deploying MigratoryData
Make sure that you have Java version 8 or later installed. Download the platform-independent tarball
package of MigratoryData and unzip it to any folder, change to that folder and edit
the main configuration file migratorydata.conf by adding the following line:
ClusterEngine = kafka
Then, run the following command on Linux or MacOS (run the similar command with the bat extension instead of the sh
extension on Windows):
./start-migratorydata.sh
This will deploy a cluster of one instance of MigratoryData which will listen for client connections on localhost,
on the default port 8800.
The default configuration of MigratoryData contains a group of Kafka consumers with a single consumer connecting to the
Kafka cluster deployed at the address localhost:9092, and subscribing to the Kafka topic vehicles as you can find in
the configuration file integrations/kafka/consumer.properties:
bootstrap.servers=localhost:9092
topics=vehicles
consumers.size=1
Also, the default configuration of MigratoryData contains a group of Kafka producers with a single producer
connecting to the Kafka cluster deployed at the address localhost:9092, as you can find in the configuration file
integrations/kafka/producer.properties:
bootstrap.servers=localhost:9092
producers.size=1
On one hand, the Kafka consumer includes a supplementary parameter topics, meaning that
an Internet client of MigratoryData will be able to subscribe only to the subjects having as the first segment, the
Kafka topic vehicles, e.g. /vehicles/car11/temperature, /vehicles/car1/speed, etc - provided however that the
Internet client is entitled by your authorization rules to subscribe to those subjects. Multiple Kafka topics can be
configured with the parameter topics as a comma-separated list.
On the other hand, an Internet client of MigratoryData will be able to publish to any Kafka topic, without the need
to configure any parameter. For example, a message on the subject /trucks/t1/location published by an Internet client
will be automatically sent to the Kafka cluster on the topic trucks with the key t1/location, provided that the
Internet client is entitled by your authorization rules to publish on the subject /trucks/t1/location.
Testing
MigratoryData Messaging
At this stage, you can open the demo web application built with MigratoryData SDK for JavaScript and bundled with MigratoryData as follows. Start a web browser on the machine where you have installed MigratoryData and Kafka and open the following URL:
push.example.com and the port 8800 is not blocked by
the firewall, you can remotely test the installation by opening the following URL from a remote machine:
http://push.example.com:8800
This will open the welcome page of MigratoryData which contains certain docs and demos. Click on the DEMO button of
the welcome page. You should see a web page like the following one:
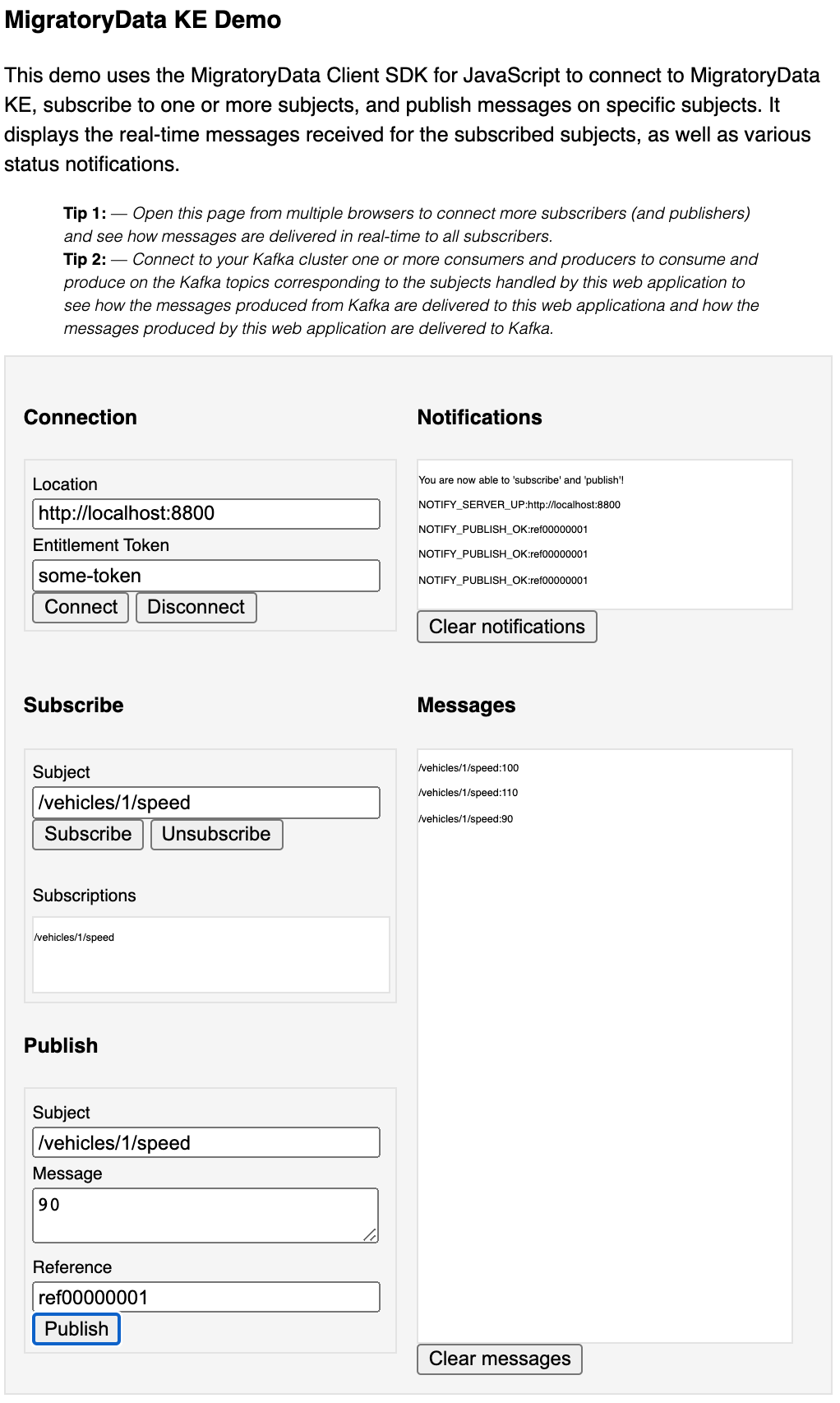
Supposing you installed MigratoryData and Kafka on your machine, click on the Connect button to connect the
demo application to your deployment. Otherwise, if you installed MigratoryData and Kafka on a remote machine,
say http://push.example.com:8800, change the Location in the demo app to
http://push.example.com:8800 before clicking on the Connect button.
Subscribe, to the subject /vehicles/1/speed by clicking the Subscribe button. You can also subscribe and unsubscribe
to and from other subjects.
Finally, publish some messages on the subject /vehicles/1/speed by clicking on the Publish button. You should see
how these messages are received in real-time. Also, you can open the demo app in another browser to see that, in fact,
the messages are delivered from the backend to all subscribers of that subject.
Kafka Messaging
By opening a Kafka consumer on the topic vehicles you will see that the messages published by the demo web app on the
subject /vehicles/1/speed are automatically received by Kafka on the topic vehicles with the key 1/speed as follows:
./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic vehicles \
--bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--consumer.config config/consumer.properties \
--property print.key=true \
--from-beginning
1/speed 100
1/speed 102
Also, you can produce messages to Kafka on the topic vehicles with the key 1/speed and see them arriving to your web
application automatically and in realtime as follows:
./bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --topic vehicles \
--bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--producer.config config/producer.properties \
--property "parse.key=true" \
--property "key.separator=:"
>1/speed:88
>1/speed:90
>1/speed:99
Conclusion
This was a quick introduction to MigratoryData. Please refer to the Configuration Guide, and Installation Guide to learn more about MigratoryData. Then, start building your realtime web and mobile apps or IoT project using your preferred programming languages to communicate with your MigratoryData cluster and your Kafka ecosystem. Please refer to the MigratoryData Client APIs and Server Extensions API for your preferred programming languages.
